Diabetic foot & Gangrene
Overview
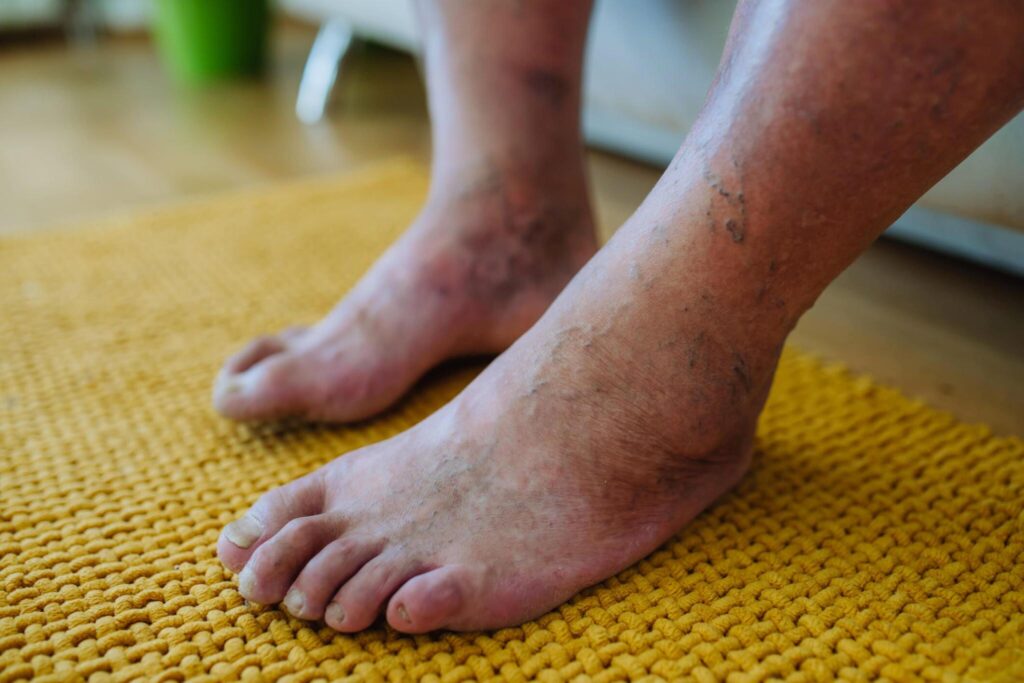
Why it's done
Prevention of Infection: Open sores or wounds in the feet can easily become infected, especially in individuals with diabetes, as their immune system may be compromised. Infection can spread rapidly and may lead to more severe complications if not addressed promptly.
Wound Healing: Diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds. Treatment aims to promote wound healing, reduce inflammation, and prevent the progression of gangrene. This may involve various medical interventions and wound care techniques.
Limbs Preservation: In severe cases of diabetic foot gangrene, there is a risk of limb amputation if the condition is not treated promptly and effectively. The goal of treatment is to preserve the affected limb and prevent the need for amputation through surgical and non-surgical interventions.
Pain Management: Gangrene can be painful, and effective treatment includes measures to manage pain and improve the patient’s quality of life. This may involve medications, physical therapy, or other pain management techniques.
Blood Sugar Control: Diabetes management is a crucial aspect of treating diabetic foot complications. Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels helps promote better wound healing and reduces the risk of further complications.
Vascular Interventions: In cases where reduced blood flow is contributing to the development of gangrene, vascular interventions such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be considered to improve blood circulation to the affected area.
Antibiotic Therapy: If there is an infection present, antibiotics may be prescribed to control and eliminate the infection. Timely and appropriate antibiotic therapy is essential to prevent the spread of infection.
Risk
- Early Detection and Diagnosis
- Glycemic Control
- Wound Care
- Infection Management
- Vascular Assessment
- Multidisciplinary Approach
- Patient Education
- Amputation Consideration
- Psychosocial Support
How do I get ready for Diabetic foot & Gangrene Treatment?
Find a Healthcare Team:
- Identify and establish a relationship with a healthcare team that specializes in diabetic foot care, including podiatrists, endocrinologists, vascular specialists, and infectious disease experts.
Gather Medical Information:
- Compile a comprehensive medical history, including details about your diabetes management, previous foot issues, surgeries, and any other relevant health conditions.
- Bring a list of your current medications, including dosages.
Undergo Necessary Tests:
- Your healthcare team may conduct tests to assess blood flow, nerve function, and the extent of the infection.
- Be prepared for imaging studies, such as angiograms or Doppler ultrasounds, to evaluate vascular health.
Maintain Glycemic Control:
- Focus on achieving and maintaining optimal blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Follow your prescribed diabetes management plan, including medications, insulin, and dietary guidelines.
Foot Care:
- Prioritize daily foot care routines, including gentle cleaning, inspection for cuts or sores, and moisturizing.
- Avoid walking barefoot and protect your feet from extreme temperatures.
Follow Prescribed Wound Care:
- If you have open wounds, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for cleaning and dressing the wounds.
- Be aware of any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, increased pain, or discharge, and report them promptly.
Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients, with a focus on foods that support overall health and wound healing.
- Engage in regular physical activity as recommended by your healthcare team.
Prepare for Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Understand that certain lifestyle adjustments may be necessary, such as changes in footwear, activity levels, and dietary habits.
- Plan for possible restrictions on weight-bearing activities or modifications in daily routines.
Communicate Openly with Healthcare Providers:
- Share any concerns, questions, or changes in your condition with your healthcare team.
- Discuss your treatment plan, including potential procedures or surgeries, and make sure you understand the expected outcomes.


