Wide Local Excision (WLE) Oral
Overview
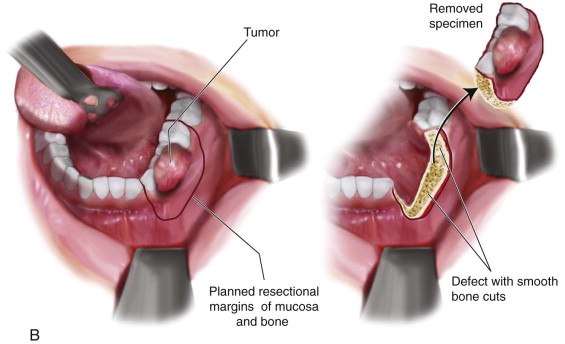
Wide Local Excision (WLE) is a surgical procedure performed to remove a cancerous or pre-cancerous lesion along with a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it.
WLE is commonly employed when there is a suspicion or confirmation of cancerous or pre-cancerous lesions in the oral cavity. It aims to remove the affected tissue along with a sufficient margin of healthy tissue to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Patients considering or undergoing Wide Local Excision for oral lesions should contact Indotaj Medical Care where doctors will consult with their healthcare team for detailed information about the procedure, personalized treatment plans, and postoperative care instructions.
Why it's done
Wide Local Excision (WLE) Oral may be recommended for several reasons, including:
- WLE is often used as a primary treatment for certain types of cancers, including skin cancer, breast cancer, and oral cancer. The goal is to completely remove the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy surrounding tissue to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- In cases where there are pre-cancerous lesions or abnormal tissue changes, WLE may be recommended to remove the affected area and prevent the progression to cancer.
- WLE is favored when precise assessment of the margins is crucial. By taking a wider margin of healthy tissue around the lesion, surgeons aim to ensure that all potentially cancerous or abnormal cells are removed.
- The size and location of a lesion can influence the choice of treatment. WLE may be preferred for lesions that are relatively smaller and well-defined.
- WLE is employed to minimize the risk of cancer recurrence. By removing a wider margin of tissue, the surgeon aims to reduce the likelihood of any residual cancer cells remaining in the treated area.
- When feasible, surgeons aim to perform WLE in a way that preserves the function and aesthetics of the affected area. This may involve reconstructive techniques, especially in areas where maintaining function and appearance is critical.
- The excised tissue is sent to a pathology laboratory for examination. This helps determine the nature of the lesion, assess whether the margins are clear of abnormal cells, and guide further treatment decisions.
Risk
Wide Local Excision (WLE) Oral can pose potential risks and complications. Some of these include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Scarring
- Changes in Sensation
- Functional Impairment
- Cosmetic Changes
- Recurrence
- Delayed Healing
- Allergic Reactions
- Adverse Reaction to Anesthesia
How do I get ready for Wide Local Excision (WLE) Oral treatment?
Preparing for Wide Local Excision (WLE) Oral treatment involves several steps to ensure a smooth procedure and recover
- Schedule a consultation with your oral surgeon or healthcare provider to discuss the need for Wide Local Excision. During this visit, your medical history, overall health, and the specifics of the oral lesion will be evaluated.
- Complete any necessary diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or biopsies, as recommended by your healthcare provider. These tests help in planning the surgery and understanding the characteristics of the oral lesion.
- Provide a comprehensive list of all medications you are currently taking, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, as well as any supplements. Your healthcare provider will guide you on whether any adjustments are needed before the surgery.
- If you are taking medications that may increase bleeding risk (e.g., blood thinners), your healthcare provider may instruct you to stop or adjust the dosage before the surgery. Follow these instructions carefully.
- Typically, you will be instructed not to eat or drink anything for a specific period before the surgery. Follow fasting guidelines provided by your healthcare team to prepare for anesthesia.


