Atrial Fibrillation
Overview
We understand the significance of Atrial Fibrillation (AF), a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and often rapid heartbeat. Our comprehensive overview of AF encompasses its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We emphasize the importance of early detection through electrocardiogram (ECG) tests and Holter monitoring, followed by personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs. With a focus on holistic care and cutting-edge interventions such as medications, cardioversion, and catheter ablation, we strive to optimize patients’ quality of life while managing their AF effectively and safely.
Why it is done?
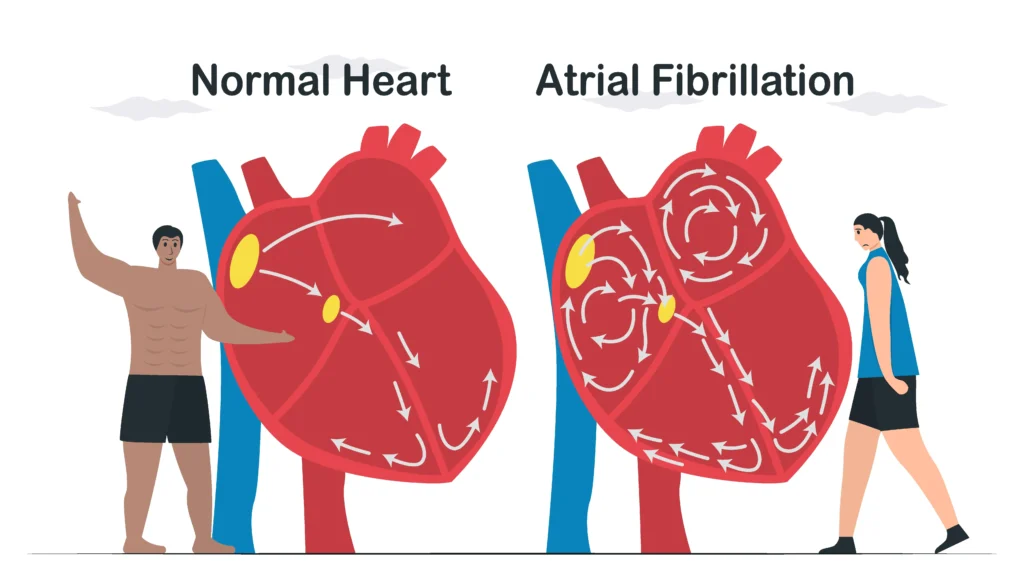
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is not something that is “done” intentionally; rather, it is a medical condition that occurs due to abnormalities in the heart’s electrical system. AF disrupts the normal rhythm of the heart’s upper chambers (atria), causing them to quiver or beat irregularly. This can lead to various complications such as blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular issues. AF can occur due to factors such as high blood pressure, heart disease, thyroid disorders, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and aging. Treatment aims to control the heart rate, restore normal heart rhythm, and prevent complications.
Symptoms of Atrial fibrillation
Common symptoms are:
- Heart palpitations or a subjective sensation of fluttering or excessive speeding up of the heart.
- Breathlessness – both at rest and especially worse on exertion
- Lightheadedness or dizziness and rarely loss of consciousness
- Tiredness and lethargy
- Very occasionally atrial fibrillation can also cause chest discomfort or tightness and this usually gets worse on exertion.
How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is diagnosed through a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. During the medical history review, the healthcare provider will inquire about symptoms, past medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors. Physical examination may reveal irregular heartbeats or other signs of heart problems. Diagnostic tests commonly used to confirm AF include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect irregularities indicative of AF.
Holter monitor or event monitor: These portable devices record heart rhythm over a period of time, allowing for the detection of intermittent AF episodes.
Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart’s structure and function, helping to identify underlying heart conditions that may contribute to AF.
Blood tests: These may be conducted to check for thyroid function, electrolyte imbalances, and other conditions that can trigger or worsen AF.


