Keloid-Scar Removal Treatment
Overview
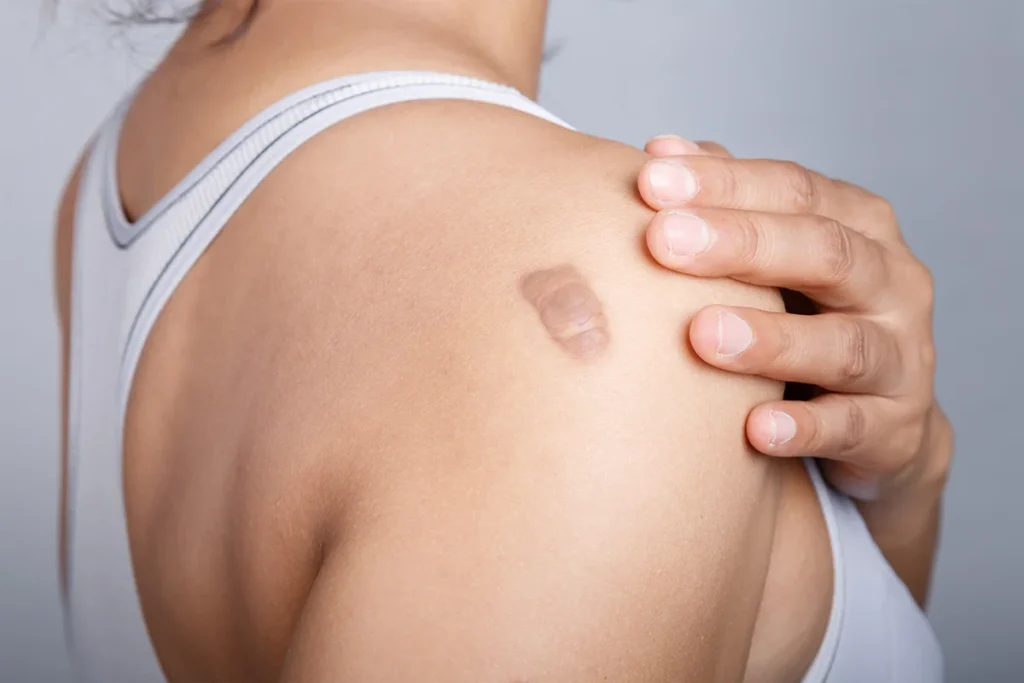
Why it's done
- Reducing Discomfort: Keloid scars can be itchy and uncomfortable, impacting daily life and self-esteem.
- Improving Appearance: Keloids are often conspicuous and may cause self-consciousness; removal aims to restore a more natural appearance.
- Alleviating Pain: In some cases, keloids may cause pain or tenderness, which removal treatments can alleviate.
- Enhancing Mobility: Large keloids may restrict movement, especially if located over joints; removal can improve mobility.
- Preventing Complications: Keloids may become infected or cause complications such as contractures; removal reduces these risks.
- Boosting Self-Confidence: Eliminating keloids can boost self-confidence and improve mental well-being.
- Addressing Functional Impairments: Keloids in certain locations, such as the earlobes, may interfere with wearing jewelry or glasses; removal restores function.
Risk
- Recurrence
- Hyperpigmentation
- Hypopigmentation
- Infection
- Pain and discomfort
- Scarring
- Allergic reactions
How do I get ready for Keloid-Scar Removal Treatment?
Consultation: Schedule a consultation with a qualified dermatologist or plastic surgeon specializing in scar removal. Discuss your medical history, including any allergies, current medications, and previous treatments.
Treatment Plan: Work with your healthcare provider to develop a customized treatment plan tailored to your specific keloid scars. Understand the chosen treatment options, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Medical Evaluation: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation to assess your overall health and suitability for the chosen treatment. This may include blood tests or other diagnostic assessments.
Stop Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting or at least refraining from smoking before and after the procedure. Smoking can impede the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
Avoid Sun Exposure: Minimize sun exposure to the treatment area in the weeks leading up to the procedure. Sunburn or tanning can increase the risk of complications and affect treatment outcomes.
Follow Pre-Treatment Instructions: Your healthcare provider will provide specific pre-treatment instructions, which may include discontinuing certain medications, avoiding blood-thinning agents like aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or applying topical creams as directed.
Arrange Transportation: If undergoing a procedure requiring anesthesia or sedation, arrange for someone to drive you home afterward. Follow any fasting instructions provided by your healthcare provider before the procedure.
Arrange for Post-Procedure Care: Plan for post-procedure care, including time off work or school if needed. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.


