Esophageal dilatation
Overview
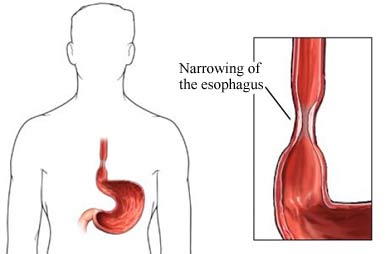
Why it's done
Esophageal Strictures: The most frequent indication for esophageal dilatation is the presence of strictures or narrowing in the esophagus. Strictures can occur due to conditions such as chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which leads to scarring and fibrosis.
Esophageal Webs or Rings: Some individuals may develop webs or rings in the esophagus, causing difficulty in swallowing. Esophageal dilatation helps in widening these narrow areas, facilitating improved passage of food and liquids.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: This is an inflammatory condition of the esophagus that can cause narrowing. Esophageal dilatation may be employed as part of the treatment plan to manage symptoms and improve swallowing function.
Achalasia: In cases of achalasia, a disorder affecting the lower esophageal sphincter, esophageal dilatation can be performed to relax the sphincter and enhance the passage of food into the stomach.
Post-Surgical Strictures: Some individuals may develop strictures in the esophagus as a result of previous surgical procedures. Esophageal dilatation can be a corrective measure in such cases.
Risk
- Perforation
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Reflux
- Tear or Stricture Formation
- Chest Pain
- Aspiration
- Reaction to Anesthesia
How do I get ready for esophageal dilatation surgery?
- Consultation with your Healthcare Provider:
- Schedule a consultation with your gastroenterologist or surgeon to discuss the details of the procedure, its purpose, and potential risks and benefits.
- Provide a detailed medical history, including any allergies, current medications, and past surgeries.
- Fasting:
- Your healthcare provider will likely instruct you to fast for a specific period before the procedure. This helps ensure that your stomach is empty, reducing the risk of complications during the surgery.
- Medication Management:
- Discuss your current medications with your healthcare provider. You may need to adjust or temporarily stop certain medications, especially blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding during the procedure.
- If anesthesia is used, your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions regarding medication on the day of the surgery.
- Allergies and Sensitivities:
- Inform your healthcare team about any allergies or sensitivities you may have, especially to medications or anesthesia.
- Arrangements for Transportation:
- Since you may receive sedation or anesthesia, arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure. It is not advisable to drive yourself on the day of the surgery.
- Clothing:
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing on the day of the procedure. This makes it easier for the medical team to place monitoring devices and provides comfort during recovery.
- Valuables:
- Leave valuables, including jewelry and accessories, at home.
- Post-Procedure Arrangements:
- Plan for a period of rest and recovery after the procedure. You may not be able to resume normal activities immediately, so ensure you have adequate support at home.
- Questions and Clarifications:
- Ask any remaining questions you may have about the procedure, recovery, and potential complications. Make sure you fully understand the process and what to expect.


