Tympanoplasty
Overview
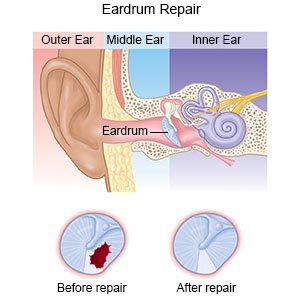
At Indotaj Medical Center, tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at addressing ruptured eardrums. The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, serves as the barrier between the ear canal and the middle ear. When a rupture occurs, creating a hole in the eardrum tissue, it impedes the vibration of the eardrum, potentially affecting hearing.
While conservative treatments like ear drops or antibiotics are often used initially, tympanoplasty may be recommended if the eardrum fails to heal within two or three months. This surgical intervention becomes necessary to prevent complications such as hearing loss, chronic infections, and dizziness.
Tympanoplasty, performed by our healthcare providers, involves accessing the eardrum and patching the hole to facilitate proper healing. Studies indicate that tympanoplasty is successful in treating ruptured eardrums in 93% of individuals undergoing the surgery at our medical center.
Why it's done
- When conservative treatments such as ear drops or antibiotics fail to heal a ruptured eardrum over a period of two to three months, tympanoplasty may be considered.
- Untreated ruptured eardrums can lead to complications such as hearing loss, chronic ear infections, and dizziness. Tympanoplasty aims to prevent or minimize these potential complications.
- A ruptured eardrum can significantly impact hearing by disrupting the normal vibration of the eardrum. Tympanoplasty seeks to restore the vibrational function of the eardrum and improve hearing.
- Chronic ear infections can arise from persistent eardrum perforations. Tympanoplasty helps in closing the hole, reducing the risk of recurrent infections and associated discomfort.
- A perforated eardrum can make the ear more susceptible to water entry, increasing the risk of infections. Tympanoplasty aims to create a barrier against water penetration, reducing the likelihood of infection.
- Individuals who experience barotrauma, often due to changes in air pressure (e.g., during air travel or scuba diving), may benefit from tympanoplasty to repair the eardrum and prevent future episodes.
- Tympanoplasty contributes to the overall health of the ear, promoting proper functioning and reducing the risk of complications associated with a perforated eardrum.
- Restoring the integrity of the eardrum through tympanoplasty can lead to an improvement in the overall quality of life, especially in terms of hearing ability and reduced susceptibility to ear-related issues.
Risk
- Hearing Changes
- Infection
- Persistent Perforation
- Graft Failure
- Tinnitus (Ringing in the Ears)
- Dizziness or Vertigo
- Changes in Taste
- Anesthesia Risks
- Scarring and Adhesions
- Incomplete Closure
- Facial Nerve Injury
How do I get ready for Tympanoplasty treatment?
- Schedule a consultation with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist who will evaluate your condition and determine if tympanoplasty is the appropriate treatment.
- Provide a comprehensive medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, allergies, and medications you are currently taking. Discuss any over-the-counter or herbal supplements as well.
- Undergo diagnostic tests, such as a hearing test (audiogram) and imaging studies, to assess the extent of the eardrum perforation and its impact on hearing.
- Engage in discussions with your healthcare team to understand the benefits, risks, and potential outcomes of tympanoplasty. Explore alternative treatments if applicable.
- If anesthesia is required for the procedure, schedule a consultation with the anesthesia team to discuss your medical history, any previous experiences with anesthesia, and address any concerns.
- Follow any preoperative instructions provided by your healthcare team. This may include fasting before surgery, avoiding specific medications, and other guidelines to ensure a safe procedure.
- Since tympanoplasty may involve anesthesia, arrange for someone to drive you home after the treatment. Anesthesia can temporarily affect your ability to drive.
- Inform your healthcare team about any existing medical conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, and ensure they are well-managed before surgery.


